At SterlingMedicalCenter.org, our medical team is committed to providing evidence-based insights into natural compounds that support health and wellness. Quercetin, a potent antioxidant found in various fruits, vegetables, and grains, has attracted attention for its potential to reduce inflammation, support immune health, and promote cardiovascular and cognitive wellness. This comprehensive guide explores quercetin’s health benefits, potential side effects, recommended dosage, and top food sources, offering practical advice for integrating this powerful flavonoid into your wellness routine.
What is Quercetin?
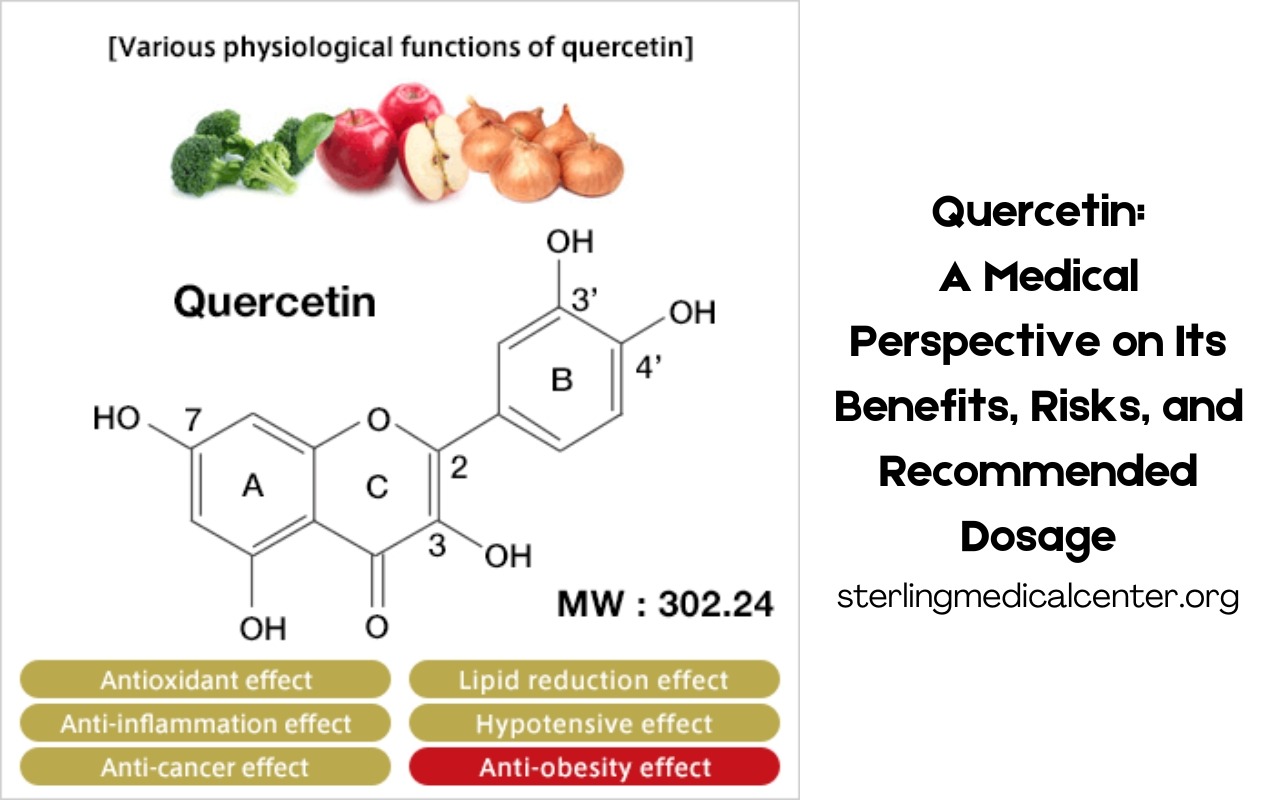
Quercetin is a naturally occurring flavonoid, a type of plant pigment responsible for the vibrant colors of many fruits and vegetables. It is not only a valuable dietary antioxidant but also contributes to overall health by combating oxidative stress and inflammation.
Natural Sources of Quercetin
Quercetin is abundant in:
- Fruits: Apples, grapes, berries (blueberries, cranberries, raspberries), and citrus fruits.
- Vegetables: Onions (especially red and white varieties), broccoli, kale, and asparagus.
- Grains and Seeds: Buckwheat and capers.
- Beverages: Green tea, black tea, and red wine.
This flavonoid is available in both natural food forms and as dietary supplements, commonly found in capsules or powder formulations.
Health Benefits of Quercetin
1. Reduces Inflammation
Quercetin's anti-inflammatory properties help modulate the body's inflammatory response. Research suggests that it inhibits inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which may reduce symptoms in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
2. Supports Cardiovascular Health
Quercetin may promote heart health by improving blood vessel function, reducing blood pressure, and lowering oxidative stress. Studies show that regular intake of quercetin can decrease both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, contributing to cardiovascular wellness.
3. Boosts Immune Function
The immune-modulating effects of quercetin can enhance the body's natural defenses. It may help reduce the severity and duration of viral infections by supporting the activity of immune cells and reducing the release of histamines, which play a role in allergic responses.
4. Promotes Brain Health
Quercetin's antioxidant capabilities may protect brain cells from oxidative damage, potentially lowering the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and dementia. Animal studies suggest that quercetin may improve cognitive function and memory.
5. May Have Anticancer Properties
Preclinical studies indicate that quercetin may inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in several types of cancer, including prostate, breast, and colon cancers. While promising, more clinical studies in humans are needed to confirm these effects.
6. Enhances Exercise Performance
Quercetin may improve physical performance by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress related to exercise. It may also enhance endurance by supporting mitochondrial function in muscle cells.
Recommended Dosage of Quercetin
The appropriate dosage of quercetin depends on the intended health benefits:
- For General Health: 500 mg per day, often combined with vitamin C or bromelain to improve absorption.
- For Managing Inflammation or Allergies: 500–1,000 mg per day, split into two doses.
- For Exercise Performance: 500–1,000 mg per day, typically taken 30–90 minutes before physical activity.
Quercetin supplements often include other bioenhancers such as:
- Vitamin C: Enhances absorption and boosts immune support.
- Bromelain: An enzyme that improves bioavailability and adds anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Resveratrol and Catechins: Other flavonoids that may have synergistic effects with quercetin.
Safety and Potential Side Effects
Quercetin is generally safe when consumed through foods. As a supplement, it is well-tolerated, but high doses (over 1,000 mg per day) may lead to mild side effects such as:
- Headaches
- Digestive discomfort
- Mild tingling sensations
Precautions
- During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While quercetin-rich foods are safe, the safety of high-dose supplements during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. Pregnant and nursing women should avoid supplementation unless advised by a healthcare provider.
- Drug Interactions: Quercetin may interact with certain medications, including antibiotics and blood pressure medications. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting quercetin supplements.
Food Sources Rich in Quercetin
Incorporating quercetin-rich foods into your diet can help you achieve its health benefits naturally:
- Capers: One of the highest natural sources of quercetin.
- Onions: Especially red and white onions, which are versatile and easy to add to meals.
- Berries: Blueberries, cranberries, and raspberries not only provide quercetin but also offer additional antioxidants.
- Apples: Particularly red apples, which contribute to both immune and cardiovascular health.
- Green and Black Tea: Regular consumption of these teas can increase daily intake of quercetin.
Conclusion
Quercetin is a powerful natural compound with a broad range of potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation, supporting cardiovascular and brain health, boosting immunity, and enhancing physical performance. While whole foods provide safe and effective amounts of quercetin, supplements may offer targeted support for specific health needs.
At SterlingMedicalCenter.org, our medical team recommends incorporating quercetin into a balanced diet and considering supplementation under professional guidance to ensure safety and maximize health outcomes. For personalized advice on using quercetin and other natural supplements, schedule a consultation with our healthcare professionals today.
Also Read: Mullein Leaf Extract and Respiratory Health